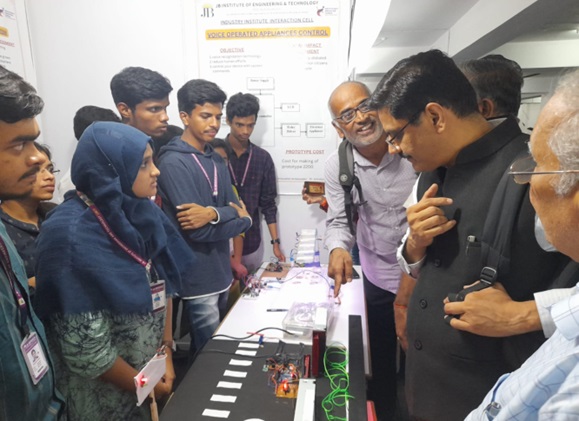
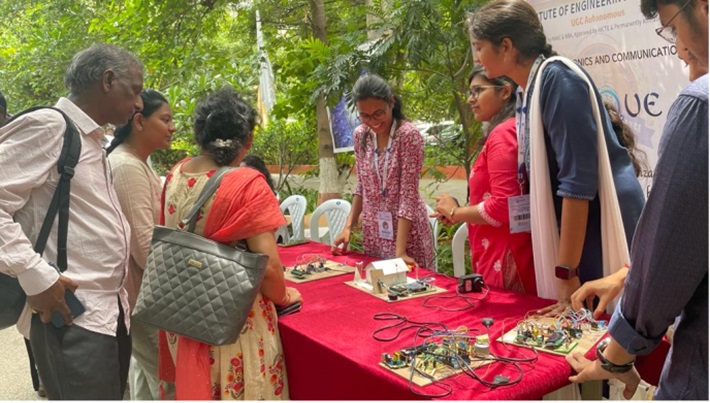
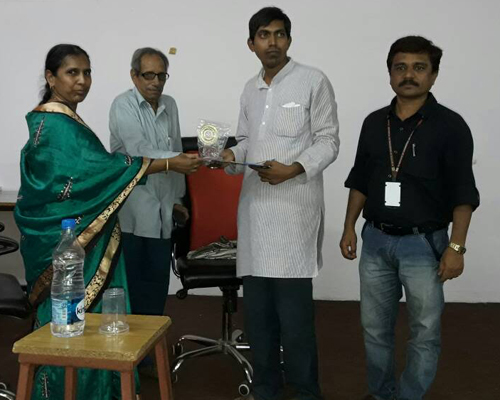
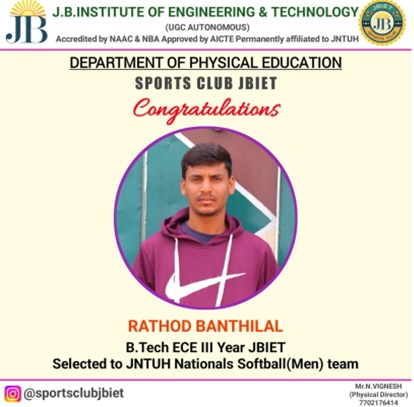
The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering was established in the year 1998 with an intake of 60 in B.Tech. The intake was increased to 90 in the year 2000 and 120 in the year 2004. The M.Tech program in VLSI System Design was introduced in 2005 with an intake of 18 and it was raised to 24 in 2014. The B.Tech. Program was accredited by NBA in 2006 and 2021.
The Department of ECE is best known for its talented and dedicated professionals renowned for their excellence in various specializations in the field of Electronics & Communication Engineering. The faculties have completed five consultancy research projects and one more project is ongoing. Faculties have patents and more than 125 research articles published in SCI/Scopus/peer-reviewed Journal and Conferences for the last 3 years. ECE Dept has received AICTE grand under MODROB, sponsored DST project of 46 Lacks and five consultancy projects of about 8.35 lacks. Granted seed money of Rs 275000/-for in house projects.
Proposal submitted to DST-SERB by Dr.Himanshu Sharma titled “IOT based remote health monitoring system for stroke using fuzzy-Deep neural network” of total budget Rs.30, 29,836 (under review)
The Department is provided with state-of-the-art technological tools incorporated in all the existing laboratories. For the last twenty-five years, the students of ECE, who walked out of the portals of the institute successfully, holding their degrees, were immediately inducted into the MNCs of high reputation in India & abroad.
HEAD OF THE DEPARTMENT

Dr. Towheed Sultana did her B.E (ECE) and M.E (PE) from PDA College of Engineering Gulbarga and Ph.D. from Anna University Chennai. Has 32 years of teaching experience. Worked in various capacities as Principal, Professor, Associate Prof and Assistant Professor. Presently working as HOD & Professor in Electronics and Communication Engineering department, J.B.Institute of Engineering Technology Hyderabad. Her areas of interest are image processing, Microprocessors, Microcontrollers and Digital logic design. Guided many projects at UG & PG level. Attended and organized workshops, FDPs, Seminars and Conferences. Presented papers in national and international journals, published Books/Book Chapters and patents, received best teacher award, chaired conference sessions, reviewed IEEE papers. Associate member of IETE and member of IEEE Chapter
Phone: 9885685836 Email: hodece@jbiet.edu.in
FACULTIES INVOLVED IN CENTRAL ACTIVITIES
|

Dr. Anindya Jana
Dean, IIIC, Moderator, EDP Cell,
Incubation Manager, i2hub,
|

Dr. Himanshu Sharma
Dean Administration
|

Dr. Md. Salauddin
Dean Academics
|

Mr. N. Ramesh Babu
ACE, PG
|
|

Dr. Prashanth Kumar Pradhan
R&D Coordinator
|
|
|
|
PROFESSIONAL BODIES
The Department of ECE has two professional bodies and one voluntary activity-based body. The Details are as follow:
|
Sl. No
|
Bodies
|
In-Charge/ Coordinator/ Branch Councillor
|
| 1 |
IEEE Student Branch (JBIET)
Year of Estd. : 2002
|
Mr Shravan Kumar
|
| 2 |
IETE (Life Membership)
Year of Estd. : 2016
|
Mr. Raj Kumar
|
| 3 |
Clique (Student Activity of ECE)
Year of Estd. : 2016
|
Mrs. K. Snehalatha
|
ACADEMIC YEAR - 2023-2024
IETE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
Workshop on Prototype/Process Design and Development
|
13.07.2023
|
VIEW
|
IEEE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
Two Days “Smart Innovation Hackathon”,
Chief Guest Rohini Naidu
|
26.08.2023 to 27.08.2023
|
VIEW
|
ACADEMIC YEAR 2022-2023
IETE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
Guest Lecture about “Image Processing and its Application”
|
8.02.2023
|
VIEW
|
|
2
|
J Bhaskar Rao Memorial 1st International Conference on Advanced Applications of Technology and Management (AATM) 2023
|
10.03.2023 to 11.03.2023
|
VIEW
|
|
3
|
Guest Lecture about “Wearable Bio-Sensors”
|
10.04.2023
|
VIEW
|
|
4
|
Three Days Workshop on “Printed Circuit Board”
|
25.04.2023to 27.04.2023
|
VIEW
|
IEEE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
Workshop on Design Thinking, Critical thinking and Innovation Design
|
11.01.2023
|
VIEW
|
|
2
|
Session on Problem Solving and Ideation Workshop
|
25.02.2023
|
VIEW
|
|
3
|
J Bhaskar Rao Memorial 1st International Conference on Advanced Applications of Technology and Management (AATM) 2023
|
10.03.2023 to 11.03.2023
|
VIEW
|
|
4
|
One Day seminar on “IEEE Digital Explorer-An Efficient Search & Resources
|
13.05.2023
|
VIEW
|
ACADEMIC YEAR 2021-2022
IETE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
Guest Lecture on "Radar Signal Processing"
|
04.09.2021
|
VIEW
|
|
2
|
Three-Day Workshop on “ Signal Processing Using MATLAB”
|
04.10.2021to 06.10.2021
|
VIEW
|
|
3
|
One week FDP on“Constructive Technologies in Electronics & Communications”
|
29.11.2021to 04.12.2021
|
VIEW
|
|
4
|
Guest Lecture on “Recent Trends and Real Time Application of Computer Networks”
|
15.06.2022
|
VIEW
|
IEEE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
A Two Day National Online Workshop on Python Programming
|
12.07.2021 to 13.07.2021
|
VIEW
|
|
2
|
One-day webinar on “science of success”
|
05.08.2021
|
VIEW
|
|
3
|
Expert Talk “Launch of 5G services”
|
01.10.2022
|
VIEW
|
|
4
|
One week workshop onARDUINO
|
21.10.2021to 27.10.2021
|
VIEW
|
ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021
IETE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
One day seminar on “IOT”
|
21.01.2021
|
VIEW
|
|
2
|
Seminar on “FBG – Fiber Bragg Gratings”
|
17.03.2021
|
VIEW
|
IEEE EVENTS
|
SL.NO.
|
NAME OF THE EVENT
|
DATES
|
DETAILS
|
|
1
|
Three Days workshop on “Eradicating pandemic effects with the effect of 5Q”
|
23.07.2020 to 25.07.2020
|
VIEW
|
|
2
|
One week Intensive teaching workshop
|
18-05-2020 to 22-05-2020
|
VIEW
|
|
3
|
Latest wireless and Computing Technologies
|
21.11.2020 to 23.11.2020
|
VIEW
|
|
4
|
Workshop on Emerging technologies on 5G Communication Observing World Telecommunications Day
|
17.05.2021
|
VIEW
|
Some of the remarkable activities conducted under IEEE SB are:
|
S.No
|
Academic Year
|
Event Name
|
|
1
|
2019-20
|
A Three Days Online National Workshop On ‘Eradicating Pandemic Effects with the Help of 5Q’, 23-07-2020 to 25-07-2020.
|
|
2
|
Online Webinar Conducted on “Research Insight of Deep Learning and Scope for ECE and EEE”,19-06-2020
|
|
3
|
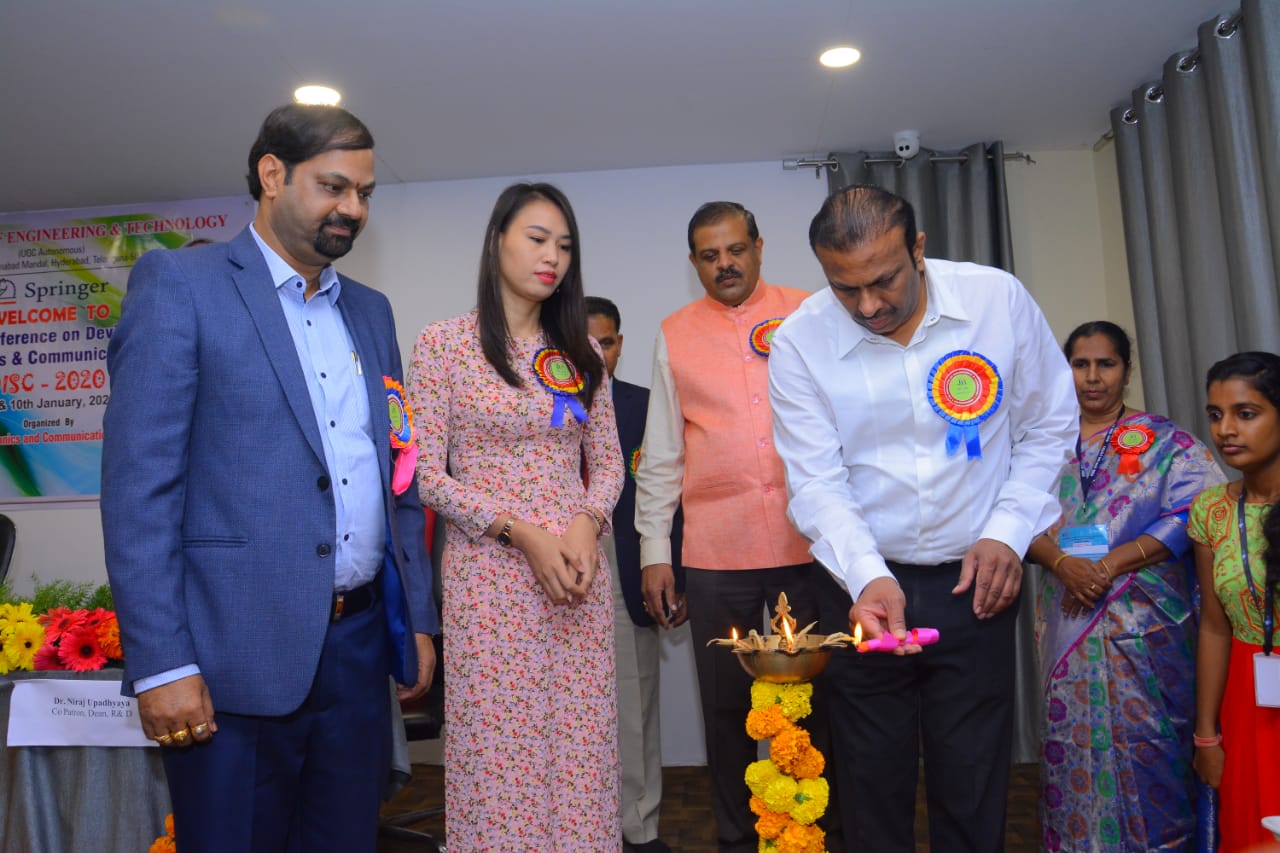
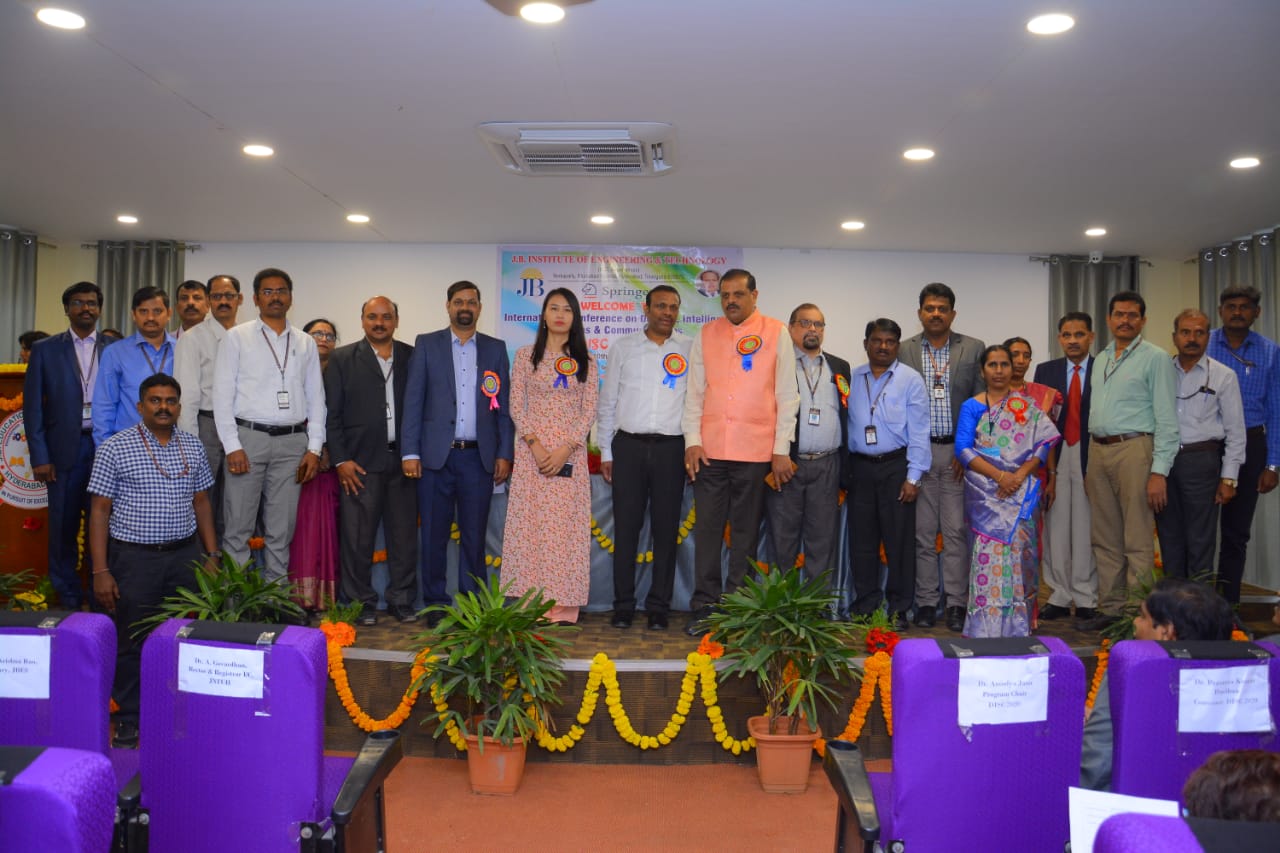
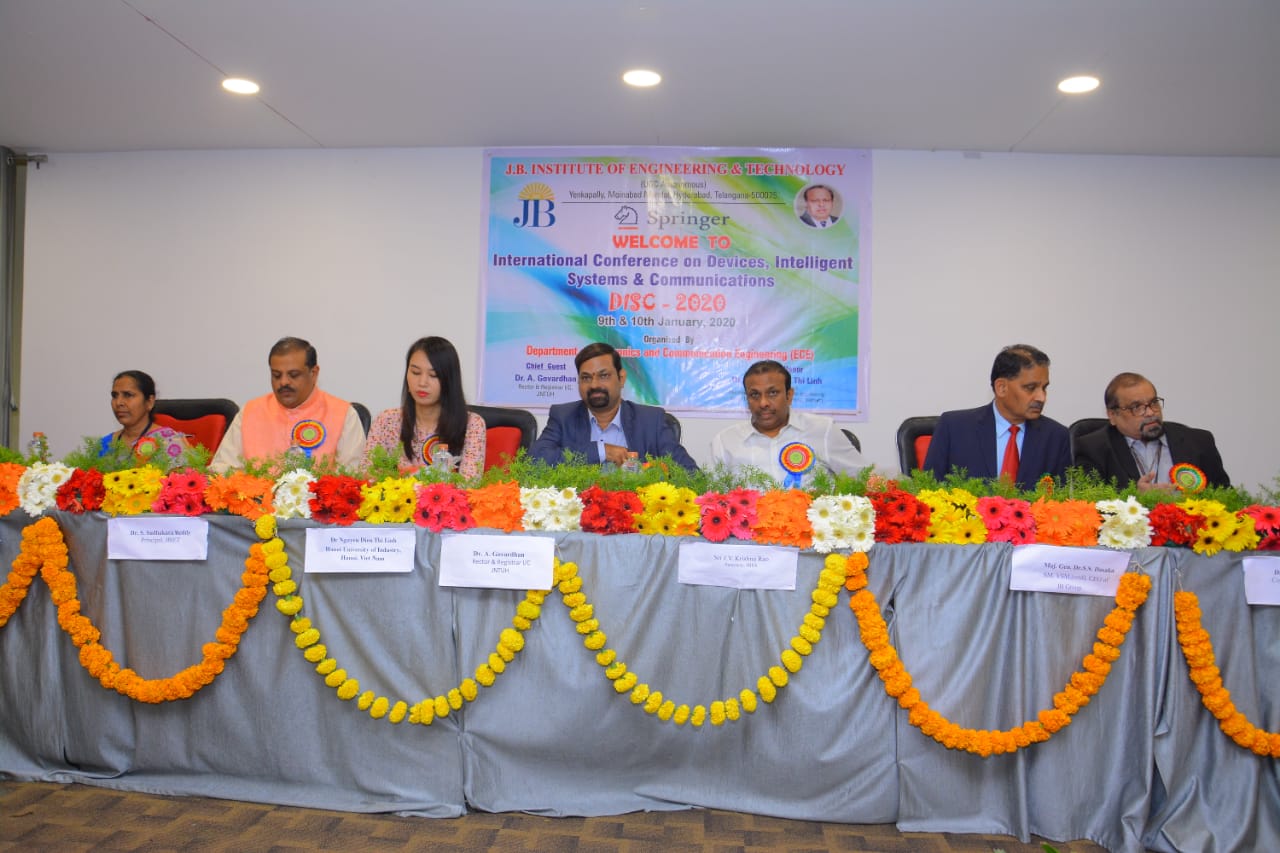
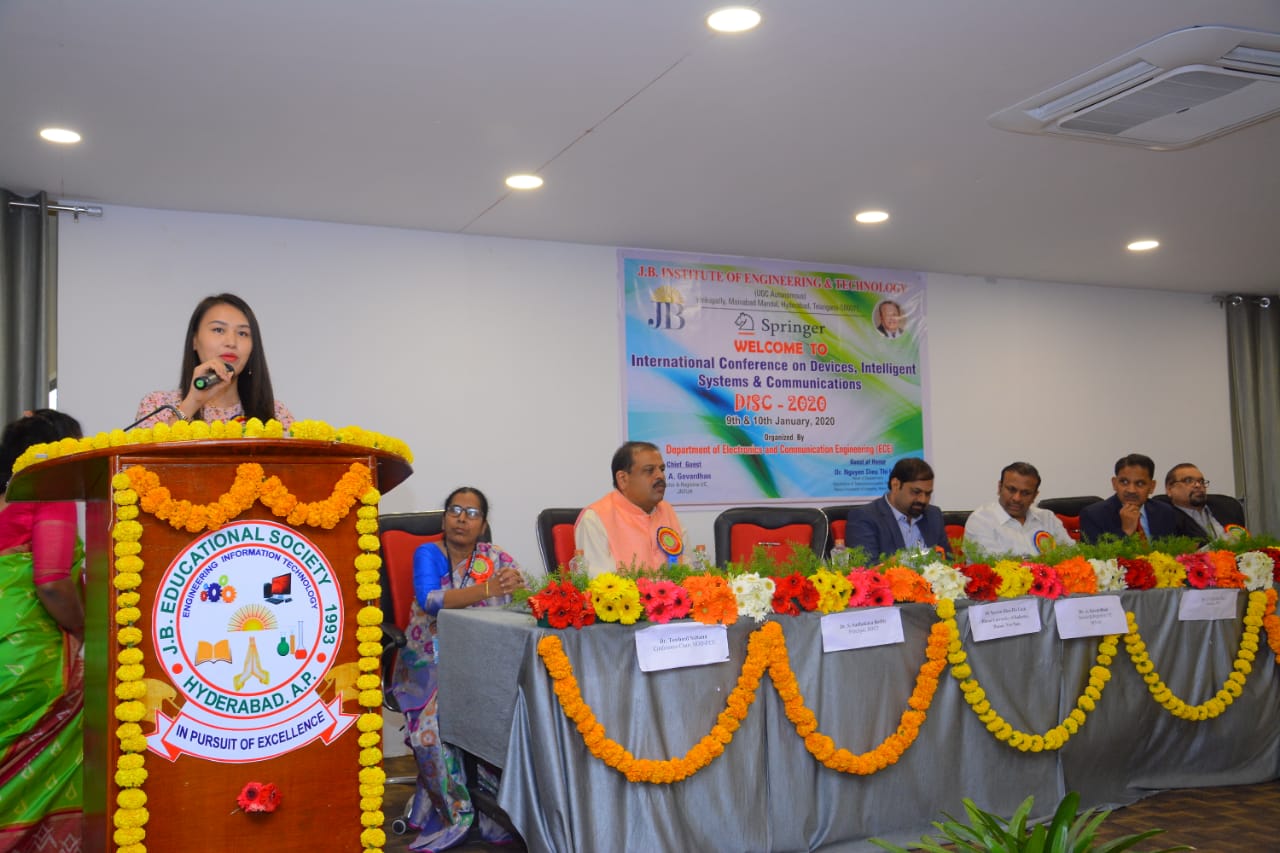
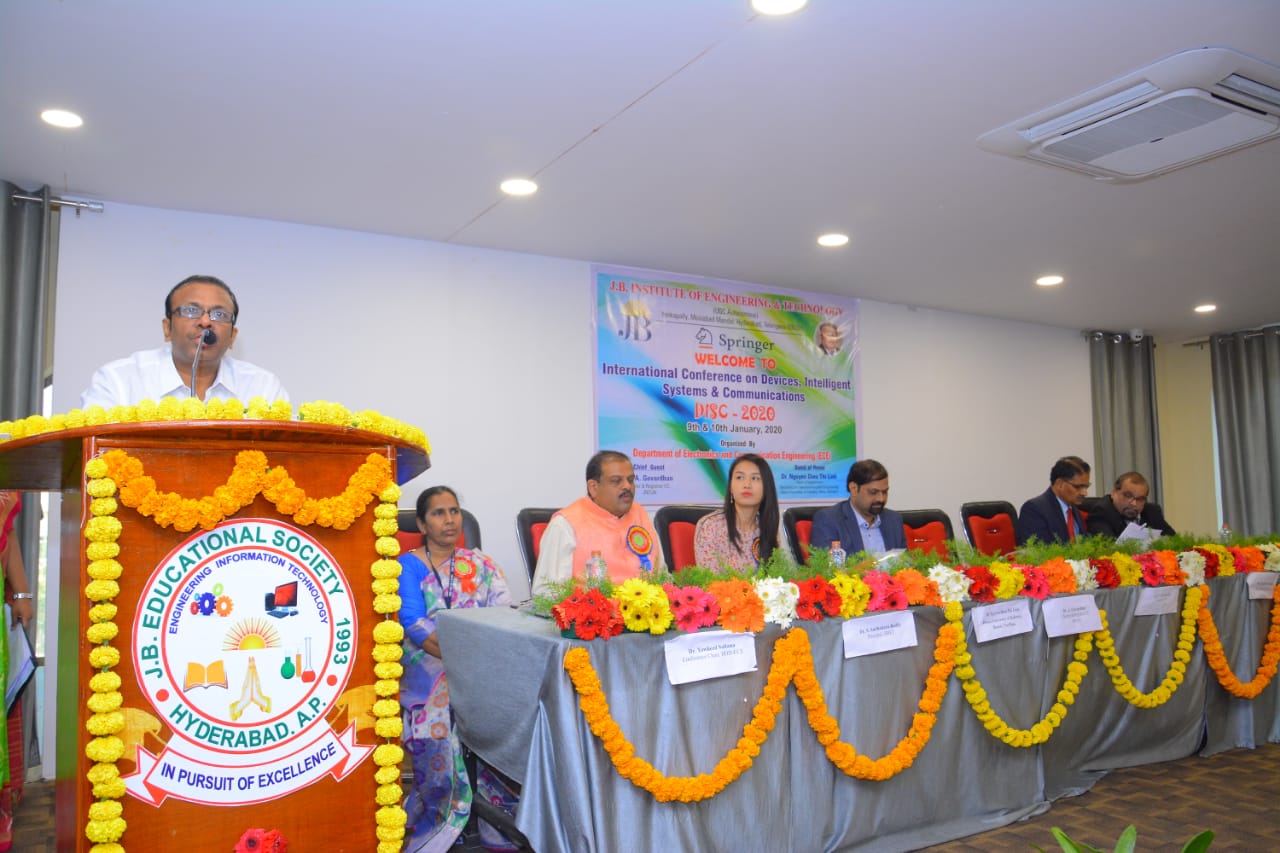
International Conference on Devices, Intelligent Systems on Communications
9-01-2020 to 10-01-2020
|
|
4
|
2018-19
|
Guest Lecture On ‘Digital Piracy And Computation Without Power Dissipation’ 28-07-2018.
|
|
5
|
Speech Processing Workshop,5-10-2018 to 7-10-2018
|
|
6
|
IOT Workshop, 28-9-2018 to 29-09-2018
|
|
7
|
Technical Talk On” Digital Design With FPGA By Using XILINX IP Cores”
07-07-2018
|
|
8
|
2017-18
|
IEEE Student Chapter Inauguration, 20-04-2018
|
Some of the remarkable activities conducted under IETE are:
|
S.No
|
Academic Year
|
Event Name
|
|
1
|
2019-20
|
One Week FDP On “Pedagogical Research,Technical Writing & Publications” 01-8-2019 to 06-08-2019.
|
|
2
|
Online Webinar Conducted on “Research Insight of Deep Learning and Scope for ECE and EEE”19-06-2020.
|
|
3
|
2018-19
|
Workshop on Advancement of Science and Technology, 15-3-18 to 17-3-2018.
|
|
4
|
2017-18
|
Seminar On Satellite Communications on 30-01-2017.
|
|
5
|
One Week National Workshop On “MATLAB And Its Applications (MIA)”, 01-06 May 2017.
|
CLIQUE is a Technical body of students with coloration of faculty of ECE. It was started in the year 2009 by a group of students from the ECE department to support the various technical and cultural activities conducted within the department. It has a membership of 480 students.
It is formed with an Objective of imparting both Technical, Soft Skills to the students across all Engineering colleges in twin Cities with students of JBIET and Social Activities like Cherish etc.
Course Material
II B.Tech
III B.Tech
IV B.Tech
LAB MANUAL
INNOVATIVE TEACHING LEARNING METHODS
The Contributions made by ECE Department Faculty towards inculcating innovative methods in Teaching and Learning are clearly elucidated both in our Department Records and on the Institute Website for peer review and critique. These methods provide scopes to enhance and reproduction of the same.
For further details click here
OSI Model Play
Some of our inclusive ways are listed below:
1. Mind Map
2. Flipped Class Room
3. e-Content Delivery
4. Activity based Learning
5. Learning By Doing
6. Digital Library
7. Content Delivery by Video lecture
8. Extension of Ph.D work (Reusability & Reproducibility)
Below are the Short Descriptions on above Innovative means in Teaching and Learning:
1. Mind Map:
A mind map is a diagram used to visually organize information. A mind map is hierarchical and shows relationships among pieces of the whole. It is often created around a single concept, drawn as an image in the center of a blank page, to which associated representations of ideas such as images, words and parts of words are added. Major ideas are connected directly to the central concept, and other ideas branch out from those.
Objectives:
1. To generate, visualize, structure and classify ideas, and as an aid to studying and organizing information, solving problems, making decisions, and writing.
2. To help students with critical and creative thinking and improve their problem-solving ability at the same time.
Outcomes:
1. The study's ability of both students and faculty will get accelerated by improving and enhancing their retention with the combination of photography and information.
2. Problem Solving Ability of students will get improved.
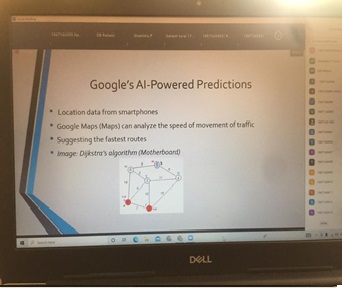
Mind Mapping:
Faculty: Dr.P K Pradhan Associate Prof.
Subject: “Image and computer vision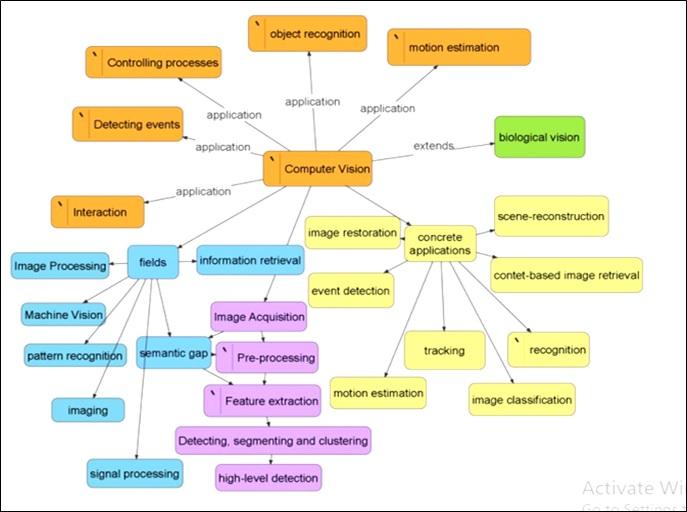
2. Flipped Class Room:
The flipped classroom is a teaching approach where our students get their first exposure to course content before coming to class through readings and video lectures. They then spend in-class time engaging in activities that we’ve designed to promote a deeper understanding of a concept.
Objectives:
1. To promote flexible learning among students.
2. To facilitate increased engagement between students and faculty.
3. To provide prompt and timely feedback to students based on their out of class assessment performance.
Outcomes:
1. Resonate well with those who are high performers and those who tend to underperform.
2. Enhance Faculty interaction with students by scheduled class meetings for dialogue.
Method: Flipped classroom
Name of the Staff: Dr Towheed Sultana
Subject Digital Electronics
Topic Flip Flops
NPTEL Video lecture no 29 and 30 were shared to students to study and to note down any doubts. The same vedio was played in the class and discussed to clear the doubts
Links of Lectures for the topic Flip Flops
http://www.infocobuild.com/education/audio-video-courses/electronics/DigitalCircuits-IIT-Kharagpur/lecture-29.html
http://www.infocobuild.com/education/audio-video-courses/electronics/DigitalCircuits-IIT-Kharagpur/lecture-30.html
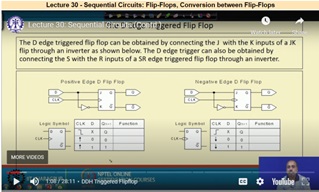
At the end of the class a quiz of 10 questions on the topic Flip Flop was conducted. The performance was amazing.
The activity helped the students do better as it included interactions and discussions which helped them to understand the topic better.
At the end of the class a quiz of 10 questions on the topic Flip Flop was conducted. The performance was amazing.
The activity helped the students do belter as it included interactions and discussions which helped them to understand the topic better.
3. e-Content Delivery
E-Resources Subscriptions links
4. Activity based Learning
The activity method is a technique adopted by a teacher to emphasize his or her method of teaching through activity in which the students participate rigorously and bring about efficient learning experiences. Learning by doing is the main focus of this method. Learning by doing is imperative in successful learning since it is well proved that more the senses are stimulated, the more a person learns and longer he/she retains.
Objectives:
1. To enhance the creative aspect of the experience.
2. To build the student’s self-confidence and to develop understanding through work in their group.
Outcomes:
1. Happy relationships between students and students, teachers and students will be developed.
Method: Activity Based Learning
Name of the Faculty: Mrs. K. Shilpa
Name of the Subject: Signals & Systems
Year & Semester: II Year I Semester


Process: Shifting of impulse function
Shifting of Impulse signal is been explained with an activity, if original signal function of t at 0 on x-axis is been operated with t-1 then it will be shifted to the Right as shown similarly for t+1 operation signal will be shifted to the left as depicted in a picture.
5. Learning by doing:
Department has two dedicated labs for implementing “Learning by doing” methodology. In these labs, students are provided with hands-on training for the better learning experience. Labs and classes are held together to implement “Learning by doing”.
Method: Learning by doing
Name of the Faculty: Ms. Jyothi
Name of the Subject: BEEE
Year & Semester: I Year I Sem


Process: Students are performing the common emitter base configuration characteristics and observing how the operating point on the load line will affect the amplification factor.
6. Digital Library:
JBIET is having a Digital Library facility. It is equipped with the Intel Tidal Data server having storage of 4 TB Capacity. 500 users can access simultaneously.
It is having the following features:
• Tidal Data Server
• Unified Library Server
• NAS
• SAN
• Jukebox
• SATA Disks 1000 GB
• Storage Router
• e-Learning Video Server Streamer
• Mail Server
• Proxy Server
• Print Server
• Server Management Software
• Client Access Manager
• 500 users capacity
7. Content Delivery by Official College Website:
Study materials of the Courses are made available online in our official web site. www.jbiet.edu.in
8. Reproducibility of Ph.D. Work
Ph.D. holders of the department motivate students and staff for brainstorming future ideas on the existing Ph.D. works.
Name of the Faculty: Dr. Anindya Jana
Dept.: Electronics & Communication Engineering
Designation: Professor & Dean- IIIC
Title: Modeling of Nanoscale Devices & Exploring their Applications
Abstract:
Since, the beginning of the seventies, the microelectronics industry has followed Moore’s law, doubling processing power energy in every eighteen months. This performance increase has been achieved by improving the speed and decreasing both the power consumption and size of devices and circuits. Recent advances in crystal growth techniques like fine line lithography, metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) and molecular beam epitaxy have made possible the fabrication of low dimensional semiconductor structures. The possibility of realization of high speed devices using such low-dimensional structures has stimulated active research in quasi-low dimensional structures. Continuous evolution in technology over the years has shrunk devices and systems so much that these dimensions are now less than a 1/10th of a micron. The term nano electronics is therefore used instead of microelectronics. The planar silicon metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) is perhaps the most important invention in the field of micro electronics. MOSFET performance has been improved at a dramatic rate via gate length scaling and is the dominating technology for integrated circuits. For long channel devices, dimensions and supply voltages are scaled by the same factor in order to maintain a constant electric field to achieve the specifications. Modern short channel devices use both the supply voltage and device geometry scaling by different factors. Moore’s prediction has held over the last four decades and will continue as long as the cost of a transistor continues to drop in price.
For more than two decades the rapid progress in complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) technology has taken place through the tremendous pace of scaling, leading to an enormous increase in speed and functionality of electronic devices. It is becoming increasingly difficult to meet MOSFET performance gains with reasonable device leakage. Now the gate leakage current constitutes a major part of the power budget of microprocessors. Another critical scaling issue involves the increase of the source-drain resistance resulting from the need for ultra-shallow p-n junctions in the source-drain regions. To keep the source-drain series resistance at a reasonable fraction of the total channel resistance, several alternative MOSFET structures have been proposed, such as non-overlapped gate structures, which do not require ultrashallow source-drain functions or structures with metallic source and drain electrodes to minimize the series resistance. Continuous device performance improvement is possible only through a combination of device scaling, new device structures and material property improvement to its fundamental limits. Retaining the same functional efficiency and achieving further minimization only through device scaling, has become almost impossible for planar CMOS due to some internal physical limitations. However, there have been reports suggesting that the CMOS transistor cannot shrunk beyond certain limits dictated by its operating principle. Over recent years this realization has lead to exploration of possible successor technologies with greater scaling potential such as quantum and single electronics for the next generation VLSI/ULSI circuits.
The single electron tunneling (SET) technology is one of the most promising future technologies to meet the required increase in density, performance and decrease in power dissipation. While the prospect of CMOS devices being completely replaced by SET devices remains to be seen. SET devices and circuits have received tremendous attention in the research community. Hybridization of the SET with complementary MOS technology has attracted much attention in recent years since such integration offers new functionalities, which are very difficult to achieve either by pure CMOS or by pure SET approaches. Consequently, Silicon SETs are appearing to be more promising than metallic SETs for their possible integration with CMOS.
Spintronics is a spin based electronic device technology that combines several characteristics like low power consumption, high operating speed and high integration density, making it financially indispensable in modern electronics. Conventional electronics encode information using the electronic charge. But in Spintronics, the spin of electrons and charge are used together to represent binary data values, rather than charge alone. Because of several distinct features the possibility of developing devices that could be much smaller, consume less electricity and be more powerful for certain types of computation than is possible with system based on electronic charge transport based devices.
In view of the above declarations the candidate wants to study some nano device models and to explore some of their applications.


Session for Faculty Members


Session for Students
Peer Review and Critique: Click Here